Very Brief Intro to Phylogenetic Comparative Methods in R
Good basic intro found here, which goes into more detail than presented here.
1. Tips vs PICS vs PGLS analyses
2. A) PICs in the 'ape' package
We use the package 'ape'
library(ape)Load the tree and data for Geospiza sparrows
geodata <- read.table("../data/geospiza.txt")
geotree <- read.nexus("../data/geospiza.nex")plot(wingL ~ tarsusL, geodata)
Drop tips for which no data
geotree <- drop.tip(geotree, "olivacea")Create numeric vector for traits
wingL <- geodata$wingL
tarsusL <- geodata$tarsusLAdd rownames to allow R to associate data with correct names on tree
names(wingL) <- row.names(geodata)
names(tarsusL) <- row.names(geodata)To calculate contrasts that have been scaled using the expected variances
ContrastwingL <- pic(wingL, geotree)
ContrasttarsusL <- pic(tarsusL, geotree)Plot these
plot(geotree)
nodelabels(round(ContrastwingL, 3), adj = c(0, -0.5), frame = "n")
nodelabels(round(ContrasttarsusL, 3), adj = c(0, 1), frame = "n")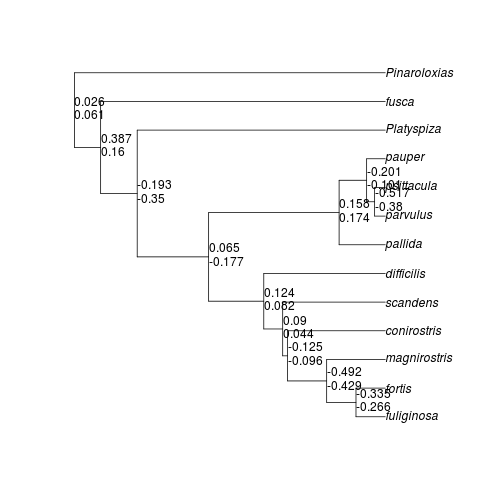
2. B) Correlated trait evolution
RegressTarsusWing <- lm(ContrastwingL ~ ContrasttarsusL - 1)
summary.lm(RegressTarsusWing)##
## Call:
## lm(formula = ContrastwingL ~ ContrasttarsusL - 1)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.1077 -0.0418 -0.0257 0.0775 0.2551
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## ContrasttarsusL 1.076 0.157 6.86 2.7e-05 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.126 on 11 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.81, Adjusted R-squared: 0.793
## F-statistic: 47 on 1 and 11 DF, p-value: 2.74e-05plot(ContrastwingL, ContrasttarsusL)
abline(RegressTarsusWing)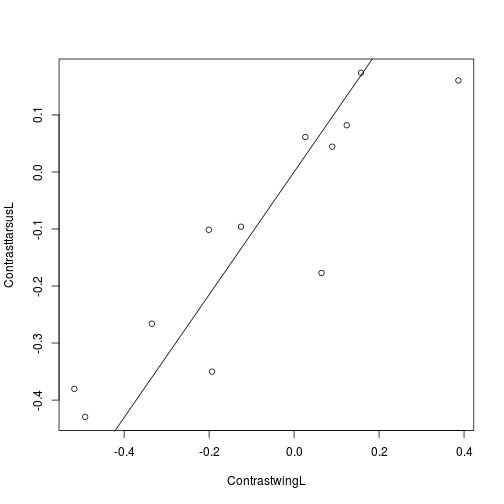
3. PGLS in the 'ape' package
library(nlme)Read in tree
geotree <- read.nexus("../data/geospiza.nex")
geospiza13.tree <- drop.tip(geotree, "olivacea")
geodata <- read.table("../data/geospiza.txt", row.names = 1)Create specific dataframe
wingL <- geodata$wingL
tarsusL <- geodata$tarsusL
DF.geospiza <- data.frame(wingL, tarsusL, row.names = row.names(geodata))
DF.geospiza <- DF.geospiza[geospiza13.tree$tip.label, ]
DF.geospiza## wingL tarsusL
## fuliginosa 4.133 2.807
## fortis 4.244 2.895
## magnirostris 4.404 3.039
## conirostris 4.350 2.984
## scandens 4.261 2.929
## difficilis 4.224 2.899
## pallida 4.265 3.089
## parvulus 4.132 2.973
## psittacula 4.235 3.049
## pauper 4.232 3.036
## Platyspiza 4.420 3.271
## fusca 3.975 2.937
## Pinaroloxias 4.189 2.980Correlation structure
bm.geospiza <- corBrownian(phy = geospiza13.tree)Model
bm.gls <- gls(wingL ~ tarsusL, correlation = bm.geospiza, data = DF.geospiza)
summary(bm.gls)## Generalized least squares fit by REML
## Model: wingL ~ tarsusL
## Data: DF.geospiza
## AIC BIC logLik
## -25.88 -24.69 15.94
##
## Correlation Structure: corBrownian
## Formula: ~1
## Parameter estimate(s):
## numeric(0)
##
## Coefficients:
## Value Std.Error t-value p-value
## (Intercept) 0.9547 0.4767 2.003 0.0705
## tarsusL 1.0764 0.1570 6.857 0.0000
##
## Correlation:
## (Intr)
## tarsusL -0.995
##
## Standardized residuals:
## Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
## -1.4607 -0.1545 0.2701 1.6376 1.9047
##
## Residual standard error: 0.09603
## Degrees of freedom: 13 total; 11 residual4. PGLS in the 'caper' package
library(caper)## Loading required package: MASS
## Loading required package: mvtnormCreate new column of names
geodata$Names <- rownames(geodata)Create comparative data object, combining the data and tree, and removing data/tips.
cdat <- comparative.data(data = geodata, phy = geotree, names.col = "Names")Test correlation of wing and tarsus as before
m <- pgls(wingL ~ tarsusL, data = cdat, lambda = "ML")
summary(m)##
## Call:
## pgls(formula = wingL ~ tarsusL, data = cdat, lambda = "ML")
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.1486 -0.0208 0.0467 0.0596 0.3356
##
## Branch length transformations:
##
## kappa [Fix] : 1.000
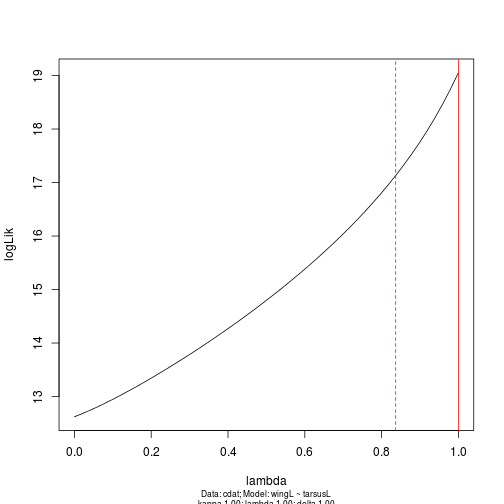
## lambda [ ML] : 1.000
## lower bound : 0.000, p = 0.00034
## upper bound : 1.000, p = 1
## 95.0% CI : (0.837, NA)
## delta [Fix] : 1.000
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 0.955 0.477 2.00 0.07 .
## tarsusL 1.076 0.157 6.86 2.7e-05 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.126 on 11 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.81, Adjusted R-squared: 0.793
## F-statistic: 47 on 2 and 11 DF, p-value: 4.08e-06Estimate phylogenetic correlation and plot it (in this case, we have a strong phylogenetic signal in the data)
m.profile <- pgls.profile(m, "lambda")
plot(m.profile)